23 10+ SQL执行性能不佳的真实案例(上)
你好,我是俊达。
在第二章 SQL优化篇的前面几讲中,我们比较系统地学习了MySQL中SQL优化的基础知识,包括索引访问的原理、优化器成本模型、表连接的几种算法、表连接顺序的计算、子查询的优化策略。在这一讲里,我整理了工作中遇到过的十多种不同类型的SQL性能问题,以案例的形式来讲解SQL优化的一些思路。
案例一:索引缺失引起的全表扫描
这是一个非常简单的SQL。
我们来看一下这个SQL的执行计划。
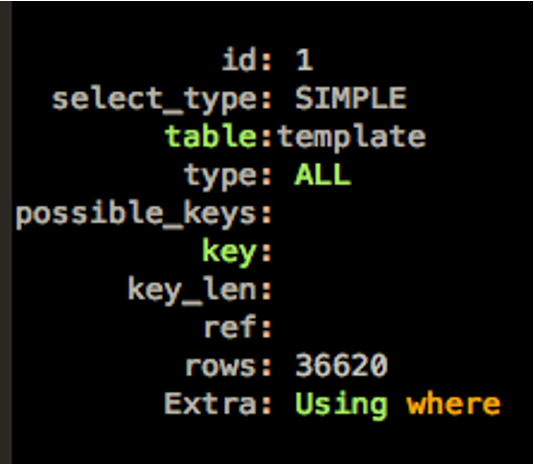
从这个执行计划里,我们要关注这些信息:
- table:访问的表,这里是template表。
- type:ALL,表示全表扫描。
- possible_keys:这个查询没有索引可以使用。
- key:查询没有使用索引。
- key_len:使用到的索引长度。
- rows:预估需要访问的数据,这里是3.6万多。
从执行计划可以看到,这个查询需要扫描3.6万行数据,没有任何索引可以使用。对于这种场景,我们可以给过滤性高的条件建立索引。
这里的关键是过滤性,如果过滤性不高,那么建了索引也不一定能提升性能。
过滤性是什么意思呢?可以理解为使用给定的where条件过滤出来的记录数占总记录数的比例,这个比例越小,那么使用索引的效果越好。我们可以用下面这个SQL来分析一个字段或多个字段的过滤性。
字段的唯一值越多,那么上面这个SQL的查询值就越小,过滤性越高。如果过滤性为1,就说明这个字段的数据都是相同的。
在有些业务场景下,可能会存在数据倾斜,某些值的数据特别多。可以用下面这个SQL来分析是否存在数据倾斜。
如果有数据倾斜,那么索引是否有效,取决于where条件中的传入的值的过滤性,过滤性高的条件组合可以用索引来提升查询效率。在这个案例中,我们建立了一个组合索引:
组合索引中字段的顺序很重要,要结合业务系统中的其他SQL来综合考虑。当然仅仅就我们案例中的这个SQL来说,字段顺序取(templet_id, status)或(status, templet_id)都可以。
案例二:优化排序操作
应用程序经常需要对访问的数据进行排序。下面这个SQL中,使用了order by。
我们来看一下执行计划。
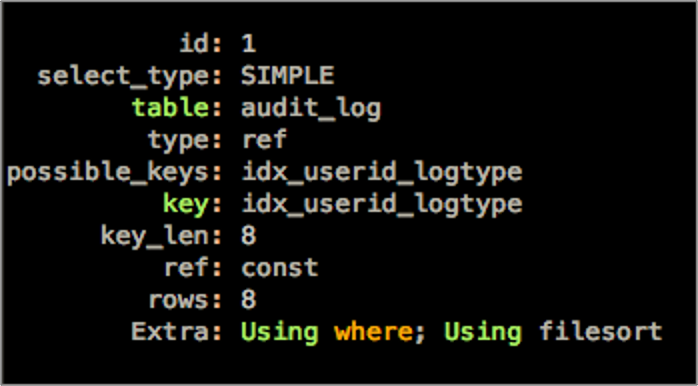
- key: idx_userid_logtype,使用了idx_userid_logtype索引。
- key_len: 8,user_id为bigint
- ref: const。
- Extra: Using where; Using filesort。
从执行计划中可以看到,SQL使用了文件排序(filesort)。排序会消耗CPU和内存资源。如果待排序的数据超过了sort_buffer_size,需要将数据写入临时文件,进行真正的文件排序。
类似上面的这个SQL,我们可以利用索引的有序性来避免排序。在索引中加上排序字段gmt_create。
alter table audit_log
drop key idx_userid_logtype,
add KEY `idx_userid_logtype` (
`user_id`,`log_type`,`gmt_create`);
查看执行计划,可以看到Extra中没有了filesort了。
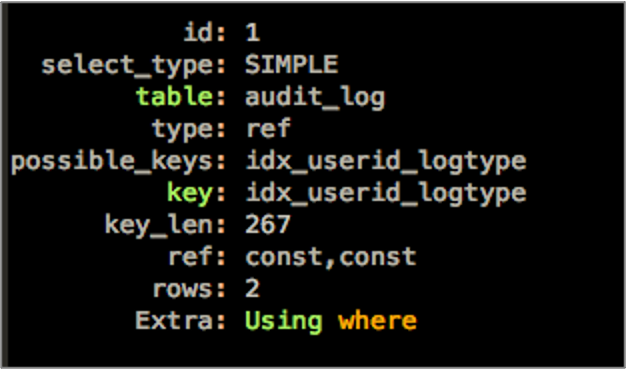
SQL需要满足几个条件,才能使用索引来消除排序。
- 排序字段前面的字段(这个例子中是user_id, log_type),需要以等值条件传入到where条件中(user_id=xx and log_type=xx)。
- 如果按多个字段排序 (order by col_1, col_2),那么索引中这几个字段也要以同样的顺序建立,idx(col_1, col_2)。
对于例子中的这个索引 idx(user_id, log_type, gmt_create),如果SQL缺少log_type的条件,就无法使用索引来消除排序了。
案例三:函数运算导致无法使用索引
有的时候,明明字段上已经建立了索引,但是查询还是无法使用索引。其中有一种情况是因为SQL中对索引字段进行了函数运算。下面就是一个比较常见的例子,SQL在gmt_modified字段上使用了date函数,用来查询当天修改过的数据。
我们来看一下执行计划。
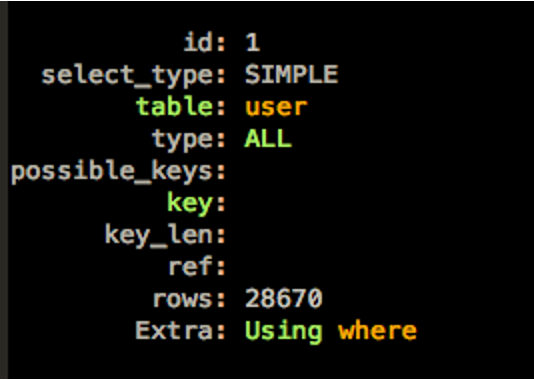
可以看到,possible_keys是空的,没有任何索引可用。实际上gmt_modified上是有索引的。但是由于where条件中对gmt_modified做了函数运算,导致无法使用索引。我们需要改写SQL,避免在索引字段上使用函数,同时还要保持SQL的逻辑不变。
这个案例中,SQL可以这么改。
select * from user
where gmt_modified >= date(now())
and gmt_modified < date(date_add(now(), interval 1 day))
这2个SQL的逻辑一样,都是获取修改时间为当天的用户信息。
我们来看一下改写后的执行计划。
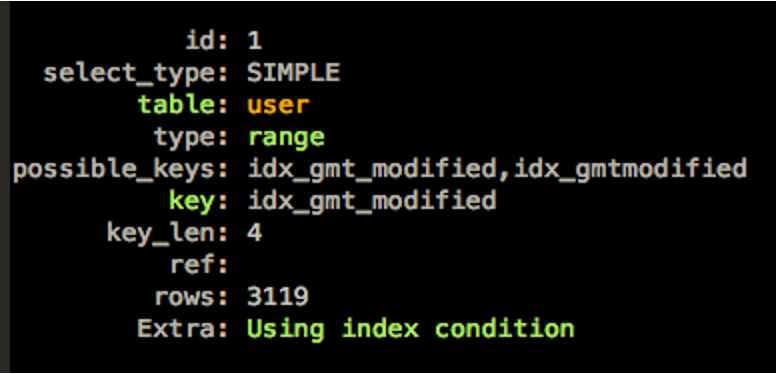 可以看到,SQL使用了idx_gmt_modified索引,扫描的记录数为3119。而之前全表扫描需要访问2.8万行数据。
可以看到,SQL使用了idx_gmt_modified索引,扫描的记录数为3119。而之前全表扫描需要访问2.8万行数据。
MySQL 8.0支持函数索引,上面这个SQL,也能用函数索引来优化。我们来做一个简单的验证,先创建一个表,写入一些测试数据,并创建一个函数索引。
mysql> create table t_date(
id int not null auto_increment,
create_time datetime,
padding varchar(2000),
primary key(id)
) engine=innodb;
mysql> insert into t_date(create_time, padding)
select date_add('2024-06-01 00:00:00', interval n hour),
rpad('x', 1000, 'abcd ')
from numbers;
mysql> alter table t_date
add key idx_createtime((date(create_time)));
下面这个SQL中,对索引字段进行了函数运算。从执行计划里可以看到,SQL用到了索引。
mysql> explain select * from t_date
where date(create_time) = '2024-06-01';
+----+-------------+--------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_date | ref | idx_createtime | idx_createtime | 4 | const | 24 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+--------+------+----------------+----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */
select `rep`.`t_date`.`id` AS `id`,
`rep`.`t_date`.`create_time` AS `create_time`,
`rep`.`t_date`.`padding` AS `padding`
from `rep`.`t_date`
where (cast(`create_time` as date) = '2024-06-01')
索引字段上的函数运算还会以其他形式出现,比如下面这两个SQL。
案例四:隐式类型转换
从上一个案例中我们已经知道,字段上的函数运算会导致SQL无法使用索引。有些情况下,虽然没有显式地对字段进行运算,但由于字段和传入的参数的数据类型不一致,数据库会进行隐式类型转换,这也会导致索引不可用。
下面是隐式类型转换常见的几种情况。
- 字段类型为varchar,存储了数字,where条件中传入了数字类型的参数。
- 字段类型为varchar,存储了日期信息,where条件中传入了日期类型的参数。
- 字段类型和传入的参数都是varchar类型,但是字符集不匹配。
- 表连接时,连接字段在2个表中的类型不一致,或字符集不一致。
我们用一个例子来验证哪些情况下,隐式类型转换会导致索引不可用。
CREATE TABLE `tab` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`phone` varchar(13) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone2` bigint DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time2` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_phone` (`phone`),
KEY `idx_phone2` (`phone2`),
KEY `idx_createtime` (`create_time`),
KEY `idx_createtime2` (`create_time2`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4
情况1:索引字段为varchar,传入数字类型的参数,索引不可用。从warning信息中可以看到,索引不可用的原因是发生了类型转换。
mysql> explain select * from tab where phone=13512345678;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ALL | idx_phone | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 3 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings;
+---------+------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+---------+------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Warning | 1739 | Cannot use ref access on index 'idx_phone' due to type or collation conversion on field 'phone' |
| Warning | 1739 | Cannot use range access on index 'idx_phone' due to type or collation conversion on field 'phone' |
| Note | 1003 | /* select#1 */ select `test`.`tab`.`id` AS `id`,`test`.`tab`.`phone` AS `phone`,`test`.`tab`.`phone2` AS `phone2`,`test`.`tab`.`create_time` AS `create_time`,`test`.`tab`.`create_time2` AS `create_time2` from `test`.`tab` where (`test`.`tab`.`phone` = 13512345678) |
+---------+------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
将传入的参数改成字符串类型,就可以使用到索引。
mysql> explain select * from tab where phone='13512345678';
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ref | idx_phone | idx_phone | 55 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
情况2:索引字段类型为varchar,传入日期类型的参数,索引不可用。从warning信息中可以看到,索引不可用的原因是发生了类型转换。
mysql> explain select * from tab where create_time = date(now());
+----+-------------+-------+------+----------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+----------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ALL | idx_createtime | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------+----------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 3 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings;
+---------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+---------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Warning | 1739 | Cannot use ref access on index 'idx_createtime' due to type or collation conversion on field 'create_time' |
| Warning | 1739 | Cannot use range access on index 'idx_createtime' due to type or collation conversion on field 'create_time' |
| Note | 1003 | /* select#1 */ select `test`.`tab`.`id` AS `id`,`test`.`tab`.`phone` AS `phone`,`test`.`tab`.`phone2` AS `phone2`,`test`.`tab`.`create_time` AS `create_time`,`test`.`tab`.`create_time2` AS `create_time2` from `test`.`tab` where (`test`.`tab`.`create_time` = <cache>(cast(now() as date))) |
+---------+------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
情况3:字段类型为数字,传入字符串类型的参数,是否也会导致索引不可用呢? 我们来测试一下。
mysql> explain select * from tab where phone2 = '13512345678';
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ref | idx_phone2 | idx_phone2 | 9 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */
select `test`.`tab`.`id` AS `id`,`test`.`tab`.`phone` AS `phone`,
`test`.`tab`.`phone2` AS `phone2`,`test`.`tab`.`create_time` AS `create_time`,
`test`.`tab`.`create_time2` AS `create_time2`
from `test`.`tab`
where (`test`.`tab`.`phone2` = 13512345678)
上面的例子中,phone2为数字类型,SQL中传入了字符串类型的参数,索引可用,因为这里类型转换发生在传入的参数上。类似的,下面这种情况也不影响索引的使用。
mysql> explain select * from tab where create_time2 = '2023-01-01';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | NULL | ref | idx_createtime2 | 6 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-----------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */
select `test`.`tab`.`id` AS `id`,`test`.`tab`.`phone` AS `phone`,
`test`.`tab`.`phone2` AS `phone2`,`test`.`tab`.`create_time` AS `create_time`,
`test`.`tab`.`create_time2` AS `create_time2`
from `test`.`tab`
where (`test`.`tab`.`create_time2` = TIMESTAMP'2023-01-01 00:00:00')
为了避免隐式类型转换导致索引不可用,我有以下几点建议。
- 设计表结构时,根据业务需求选择精确的字段类型,不要用varchar类型存储日期和数字。
- 同一个业务字段,在不同的表里面字段类型要保持一致,字符集也要保持一致。
- SQL中传入的参数要和字段的数据类型保持一致。
案例五:字符集不一致导致的隐式类型转换
执行表连接时,如果连接字段在两个表中的字符集不一致,也会发生隐式类型转换,也可能会导致索引不可用。下面这个例子就是这种情况。
SELECT *
FROM funds
WHERE uuid in (
SELECT uuid
FROM patients
WHERE create_at != "0000-00-00 00:00:00"
)
先看一下执行计划。

优化器将子查询转换成了半连接,并使用了临时表来去重(Start temporary,End temporary)。被驱动表funds的uuid上有唯一索引,但是执行计划中显示这个表没有可用的索引。查询使用BNL连接算法(Block Nested Loop)。
执行explain extended后查看warnings(注:8.0已经不支持explain extended了),发现SQL中有字符集转换的操作convert(b.uuid using utf8mb4)。
mysql> explain extended
select b.*
from patients a, funds b
where a.create_at != "0000-00-00 00:00:00"
and a.uuid=b.uuid
mysql> show warnings
select *
from patients a
join funds b
where((a.create_at <> '0000-00-00 00:00:00')
and(a.uuid= convert(b.uuid using utf8mb4)))
检查表结构后发现,两个表中uuid的字符集不一样。
CREATE TABLE `funds` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`uuid` varchar(128) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'UUID',
......,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uuid_idx` (`uuid`))
ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
CREATE TABLE `patients` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`uuid` varchar(128) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '项目uuid',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`))
ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
funds表中uuid的字符集是utf8,patients表中uuid的字符集是utf8mb4。
我们改写了SQL,使用convert函数将patients.uuid转换成utf8,载去和funds表连接,这样就避免了funds.uuid上的隐式类型转换。
explain extended
SELECT b.*
FROM (select convert(uuid using utf8) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci as uuid
from patients
where project_create_at != "0000-00-00 00:00:00") a, funds b
WHERE a.uuid = b.uuid
我们来看一下SQL改写后的执行计划,可以用到funds表中uuid的唯一索引了,type为eq_ref。

为了避免表连接时发生隐式类型转换,我建议同一个业务字段,在不同的表里,数据类型和字符集要保持一致。
优化器在转换字符集时,选择了将utf8mb3转换成utf8mb4。下面是一个测试案例,可以说明优化器的这个选择。
先创建两个测试表。
create table t_1(
id int not null auto_increment,
uuid varchar(32),
padding varchar(2000),
primary key(id),
key idx_uuid(uuid)
) engine=innodb charset utf8mb3;
create table t_2(
id int not null auto_increment,
uuid varchar(32),
padding varchar(2000),
primary key(id),
key idx_uuid(uuid)
) engine=innodb charset utf8mb4;
t_1表使用utf8mb3字符集,t_2表使用utf8mb4字符集。以t_1表作为驱动表时,可以使用t_2表uuid的索引,因为t_2.uuid没有发生类型转换。
mysql> explain select * from t_1 straight_join t_2 on t_1.uuid = t_2.uuid;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----------+---------+--------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----------+---------+--------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_1 | ALL | idx_uuid1 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_2 | ref | idx_uuid2 | idx_uuid2 | 131 | rep.t_1.uuid | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-----------+---------+--------------+------+----------+-----------------------+
2 rows in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Warning
Code: 1739
Message: Cannot use ref access on index 'idx_uuid1' due to type or
collation conversion on field 'uuid'
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */
select `rep`.`t_1`.`id` AS `id`,`rep`.`t_1`.`uuid` AS `uuid`,
`rep`.`t_1`.`padding` AS `padding`,`rep`.`t_2`.`id` AS `id`,
`rep`.`t_2`.`uuid` AS `uuid`,`rep`.`t_2`.`padding` AS `padding`
from `rep`.`t_1` straight_join `rep`.`t_2`
where (`rep`.`t_1`.`uuid` = `rep`.`t_2`.`uuid`)
以t_2表作为驱动表时,无法使用t_1表uuid的索引,因为t_1.uuid发生了类型转换。此时优化器使用了Hash连接。
mysql> explain select * from t_2 straight_join t_1 on t_1.uuid = t_2.uuid;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_2 | ALL | idx_uuid2 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_1 | ALL | idx_uuid1 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (hash join) |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 3 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Warning
Code: 1739
Message: Cannot use ref access on index 'idx_uuid1' due to type or
collation conversion on field 'uuid'
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Level: Warning
Code: 1739
Message: Cannot use range access on index 'idx_uuid1' due to type or
collation conversion on field 'uuid'
*************************** 3. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */
select `rep`.`t_2`.`id` AS `id`,`rep`.`t_2`.`uuid` AS `uuid`,
`rep`.`t_2`.`padding` AS `padding`,`rep`.`t_1`.`id` AS `id`,
`rep`.`t_1`.`uuid` AS `uuid`,`rep`.`t_1`.`padding` AS `padding`
from `rep`.`t_2` straight_join `rep`.`t_1`
where (`rep`.`t_1`.`uuid` = `rep`.`t_2`.`uuid`)
案例六:优化or条件
很多情况下,优化器可以自动选择一个最优的执行计划。但由于SQL的写法很多,在一些场景下,优化器选择的执行计划效率并不高。这时就可能需要改写SQL,帮助优化器找到更好的执行计划。where子句中不同的字段上的条件使用or相连,就比较容易引起性能问题。
下面这个SQL来自一个真实的业务系统。
SELECT count(1)
FROM car
WHERE is_deleted = 0
AND (seller_id = 100
OR (creator = 200 AND seller_id = -1))
AND car_id NOT IN (
SELECT car_id
FROM product
WHERE product_type = 2
AND source = 2)
先看一下执行计划,主查询中使用索引访问16万行数据。子查询这里只需要执行一次。

上面的SQL中,seller_id=100和creator = 200这两个条件的过滤性都不错,而且也都建了索引,但是这2个条件使用了OR。优化器最终选择了seller_id上的索引,但是seller_id = -1这个条件的过滤性并不好。
MySQL支持index_merge的执行计划,理论上可以用seller_id=100和creator=200过滤数据,再把数据合并起来,但是这里优化器并没有采用这个执行计划。因此我们将SQL做了改写,将SQL拆分成2个部分,使用union all合并数据。
SELECT sum(a) FROM (
SELECT count(1) as a FROM car WHERE is_deleted = 0 AND car_id NOT IN ( SELECT car_id FROM product WHERE product_type = 2 AND source = 2)
AND (seller_id = 100)
union all
SELECT count(1) as a FROM car WHERE is_deleted = 0 AND car_id NOT IN (SELECT car_id FROM product WHERE product_type = 2 AND source = 2)
AND creator = 1000 AND seller_id = -1
) t
看一下改写后的执行计划。
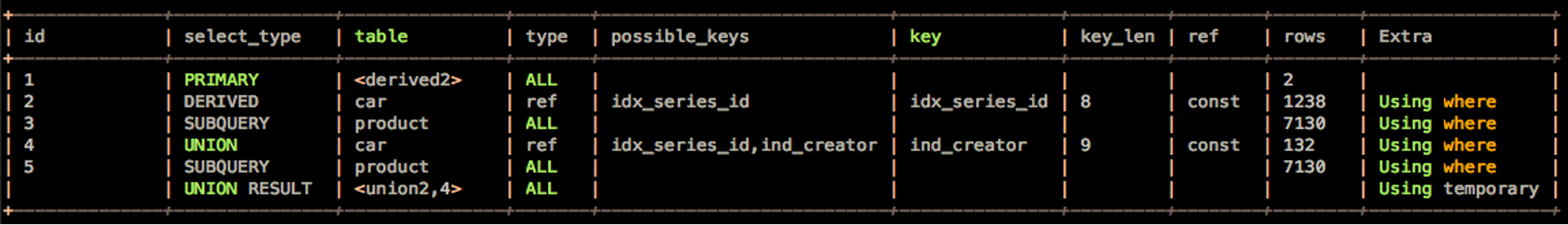
改写之后,union all的2个SQL片段使用了不同的索引,扫描的行数分别是1238和7130,比改写之前提升了一个数量级。这样改写之后,执行计划也会更稳定。
总结
这一讲的六个案例,在平时工作中比较常见,通常也比较容易解决。首先要理解索引的选择性,为查询中过滤性高的条件创建合适的索引。对于隐式类型转换,最重要的是要在建表的时候就选择精确的数据类型,避免使用varchar来存储数字类的、日期时间类的数据。字符集也要保持一致。如果表已经建好,系统已经上线运行了,那就要在应用代码里使用和字段类型匹配的数据类型。
思考题
有时候我们会遇到执行计划选择了错误的索引,导致SQL性能比较差。一个可能的解决方案是使用force index强制索引。使用force index可能会存在哪些潜在的风险?有没有其他办法来避免执行计划选错索引?
期待你的思考,欢迎在留言区中与我交流。如果今天的课程让你有所收获,也欢迎转发给有需要的朋友。我们下节课再见!
- 陈星宇(2.11) 👍(1) 💬(2)
老师,请教一个问题,就是业务上会有很多查询是可以1个条件或者多个条件,比如时间范围,状态,人员名称。正常建一个这3个字段的联合索引就行,但是有可能覆盖不到单独使用一个条件的查询,这种我们现在都是单独在每个字段上再建索引,导致空间浪费。这种有什么好的建议吗?
2024-10-14 - 美妙的代码 👍(1) 💬(1)
老师,能讲下文章结尾的问题答案吗?
2024-10-14 - Geek_c37964 👍(0) 💬(1)
mysql新人,猜一下思考题的答案:) force index 虽然暂时可以让优化器选择正确的索引,但是当数据的分布等发生变化时,可能当前的索引就不是最优的了,而这也阻止了优化器自动选择合适的索引。 优化器选错索引的情况一般是统计信息不准确导致的,所以执行语句前可以analyse一下刷新统计信息,从而让优化器选择合适的索引。 不知道思考的正不正确,还请老师解答!
2024-10-14 - 叶明 👍(0) 💬(1)
使用 force index 可能会存在哪些潜在的风险? 风险1,索引选择错误,force index 适合 SQL 中必带某些查询字段,然而现实中的 SQL 并不总是这样,如果强制走某个索引,而索引前缀字段恰好在查询条件中不存在,这会导致使用全索引扫描,比全表扫描还糟糕。 mysql> show create table t_jointab\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: t_jointab Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t_jointab` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `a` int NOT NULL, `b` int NOT NULL, `c` varchar(4000) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_a` (`a`,`b`), KEY `idx_b` (`b`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=16384 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select id, a, b from t_jointab force index(idx_a) where b = 5; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+---------------+-------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+---------------+-------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t_jointab | NULL | index | idx_a | idx_a | 8 | NULL | 8574 | 0.10 | Using where; Using index | 风险2,需要修改应用代码,有时间差,数据库的 CPU 可能已经告警一段时间,应用不可用了。 有没有其他办法来避免执行计划选错索引? 方法1,force index 里多放几个备选索引,让优化器在这几个推荐的索引中选择执行代价最小的,不过 DBA 维护起来不方便,毕竟在应用层了。 方法2,ignore index 也经常用,在 order by col_sort limit N 场景中,经常错误选择 col_sort 列来排序,而不走查询条件中列上的索引。用 ignore index 来忽略掉 col_sort 上的索引 方法3,mysql 插件 query rewrite 插件,这个避免不了执行计划选错索引,但能缩短不可用时间,阿里云也有固定执行计划的数据库层面的工具:dbms_outln.add_index_outline
2024-10-14 - 陈星宇(2.11) 👍(0) 💬(1)
用force index会存在如果索引名称变了,会导致sql性能发生变化。
2024-10-14