18 读懂MySQL中的执行计划(上)
你好,我是俊达。
上一讲我介绍了数据库中最主要的几种访问路径,不同的访问路径,在执行性能上可能会存在巨大的差别。但是我们怎么知道某一个具体的SQL语句在执行时,采用了什么样的访问路径呢?这就涉及到SQL的执行计划了。执行计划描述了SQL语句的访问路径,通过执行计划,我们可以知道:
- 表上是否有可用的索引,SQL执行时是否使用了索引,使用了哪些索引?
- 表连接的顺序是怎样的?
- 使用了哪种表连接算法,是用了Nest Loop还是Hash Join?
- 查询是否用到了临时表,是否进行了文件排序?
在MySQL中,我们使用Explain命令查看语句的执行计划。这一讲中我会使用四十多个演示SQL,来解释EXPLAIN输出信息的具体含义。至于为什么一个SQL使用了这个执行计划,而不是别的执行计划,我会在接下来的几讲中慢慢展开。
为了便于演示各种不同的执行计划,我使用了下面这些测试表和测试数据,你也可以在自己的环境中进行测试。
CREATE TABLE `digit` (
`a` tinyint NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into digit values (0),(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9);
CREATE VIEW numbers AS
select a.a*1000 + b.a*100 + c.a*10 + d.a as n
from digit a, digit b, digit c, digit d;
-- 本章中大部分案例都使用tab表
CREATE TABLE `tab` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`a` int NOT NULL,
`b` int NOT NULL,
`c` int NOT NULL,
`padding` varchar(7000) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_abc` (`a`,`b`,`c`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into tab (a,b,c,padding)
select n%3, n, n%100, rpad('x', 100, 'x')
from numbers where n < 10000;
-- t_merge主要用于演示index_merge的几种情况
create table t_merge(
id int not null auto_increment,
a int not null,
b int not null,
c int not null,
d int not null,
padding varchar(4000),
primary key(id),
key idx_ad(a,d),
key idx_bd(b,d),
key idx_cd(c,d)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into t_merge(a,b,c,d,padding)
select n % 3 + 1, n % 17 + 1, n % 19 + 1, n % 10 + 1, rpad('y', 100, 'y')
from numbers
where n between 1 and 3*17*19*10;
使用EXPLAIN命令
使用EXPLAIN命令可以查看SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、REPLACE等语句的执行计划。EXPLAIN命令的基本语法如下:
FORMAT指定了执行计划的输出格式,不指定时,默认以表格形式输出执行计划。
mysql> explain select * from tab;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9755 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
FORMAT指定为TREE时,以树的形式显示执行计划,这种显示格式和Oracle执行计划的显示方式比较像。
下面这个测试SQL中,使用了NO_SEMIJOIN提示,阻止优化器将子查询改写成表连接。你可以试一下,将提示去掉后,会使用怎样的执行计划。
explain format=tree
select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@subq1) */ *
from tab a
where id in (
select /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) */ id from tab b
)
EXPLAIN: -> Filter: <in_optimizer>(a.id,<exists>(select #2)) (cost=1031.55 rows=9913)
-> Table scan on a (cost=1031.55 rows=9913)
-> Select #2 (subquery in condition; dependent)
-> Limit: 1 row(s) (cost=0.35 rows=1)
-> Single-row covering index lookup on b using PRIMARY (id=<cache>(a.id)) (cost=0.35 rows=1)
FORMAT指定为JSON时,以JSON格式显示执行计划。JSON格式的执行计划中,可以看到一些成本的信息。
explain format=json
select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@subq1) */ *
from tab a
where id in (
select /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) */ id from tab b
)
{
"query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"cost_info": {
"query_cost": "1031.55"
},
"table": {
"table_name": "a",
"access_type": "ALL",
"rows_examined_per_scan": 9913,
"rows_produced_per_join": 9913,
"filtered": "100.00",
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "40.25",
"eval_cost": "991.30",
"prefix_cost": "1031.55",
"data_read_per_join": "264M"
},
"used_columns": [
"id",
"a",
"b",
"c",
"padding"
],
"attached_condition": "<in_optimizer>(`rep`.`a`.`id`,<exists>(<primary_index_lookup>(<cache>(`rep`.`a`.`id`) in tab on PRIMARY)))",
"attached_subqueries": [
{
"dependent": true,
"cacheable": false,
"query_block": {
"select_id": 2,
"cost_info": {
"query_cost": "0.35"
},
"table": {
"table_name": "b",
"access_type": "unique_subquery",
"possible_keys": [
"PRIMARY"
],
"key": "PRIMARY",
"used_key_parts": [
"id"
],
"key_length": "4",
"ref": [
"func"
],
"rows_examined_per_scan": 1,
"rows_produced_per_join": 1,
"filtered": "100.00",
"using_index": true,
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "0.25",
"eval_cost": "0.10",
"prefix_cost": "0.35",
"data_read_per_join": "27K"
},
"used_columns": [
"id"
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
EXPLAIN输出详解
接下来,我将以默认的表格输出形式为准,来进行介绍。在EXPLAIN的输出中,每一行表示一个查询单元。查询单元有几种情况:
- 关联查询中,每一个关联的表是一个查询单元;
- 每个子查询都会对应一个查询单元;
- 组成UNION语句的每个子句都会对应一个查询单元;
- 每个派生表对应一个查询单元。
EXPLAIN的输出中包含以下字段:
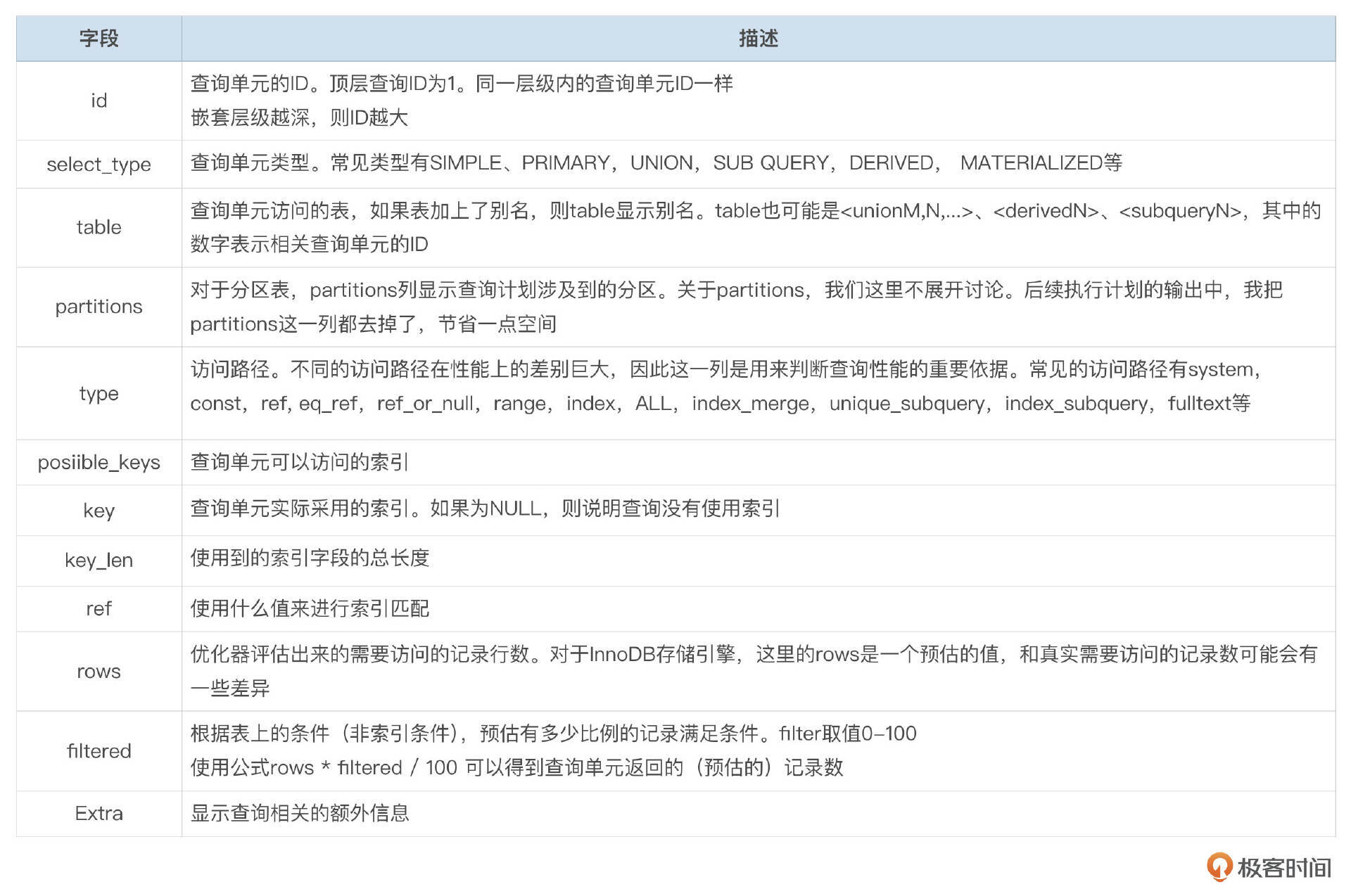
ID
ID为查询单元的编号。主查询(顶层查询)的ID为1。同一层级内,如果有表连接,则它们的查询单元ID一样。子查询的嵌套层级越深,ID越大。下面的例子中,有2个子查询,子查询2嵌套在子查询1中。
mysql> explain
select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@subq1 ) */ *
from tab ta, tab tx
where ta.id in (
select /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) NO_SEMIJOIN(@subq2) */ id from tab tb
where c in (select /*+ QB_NAME(subq2) */ c from tab tc)
)
and ta.id = tx.id
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-----------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-----------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | ta | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 1 | PRIMARY | tx | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | rep.ta.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | SUBQUERY | tb | index | PRIMARY | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
| 3 | SUBQUERY | tc | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-----------+------+----------+--------------------------+
查询中使用提示QB_NAME、NO_SEMIJOIN,是为了避免优化器使用半连接查询优化,因为使用半连接优化后,这个示例中的子查询就被优化掉了。ID为1的2个查询单元,按从上到下的顺序关联,驱动表为ta。这里Extra中没有额外的信息,说明使用了嵌套循环连接。
SELECT_TYPE
SELECT_TYPE为查询单元的类型,有以下几种可能的类型。
- SIMPLE
如果语句没有使用UNION或子查询,那么SELECT_TYPE为SIMPLE。
- PRIMARY
如果语句用到了子查询,那么最外层查询的select_type为PRIMARY,表示这是主语句。如果语句使用了UNION,则第一个查询单元的select_type为PRIMARY。
- UNION
使用UNION或UNION ALL的查询中,第二个和后续查询的select_type为UNION
- UNION RESULT
UNION RESULT表示UNION去重后的结果。下面这个例子中,ID为3的这一行就是ID为1和2这两个查询单元结果集Union之后得到的。
mysql> explain select a from tab ta union select c from tab tb;
+----+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | ta | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 2 | UNION | tb | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 3 | UNION RESULT | <union1,2> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Using temporary |
+----+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+
- DEPENDENT UNION
如果UNION子句位于子查询中,并且子查询依赖了外部查询中字段,则select_type为DEPENDENT UNION。
mysql> explain select * from tab ta where id in (
select a from tab tb union select c from tab tc);
+----+--------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | ta | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | tb | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | func | 3304 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 3 | DEPENDENT UNION | tc | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 10.00 | Using where; Using index |
| 4 | UNION RESULT | <union2,3> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Using temporary |
+----+--------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
- UNCACHEABLE UNION
union查询出现在子查询中,并且union语句使用了非确定性函数(如rand)或使用了变量,那么union查询单元的select_type为UNCACHEABLE UNION。
mysql> explain select distinct a from (
select a from tab tb
union all
select c from tab tc where c > rand()
) tx;
+----+-------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 13217 | 100.00 | Using temporary |
| 2 | DERIVED | tb | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 3 | UNCACHEABLE UNION | tc | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
mysql> explain select * from tab where exists (
select avg(b) from tab
union all
select b from tab where b > rand()
);
+----+-------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | tab | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | SUBQUERY | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 3 | UNCACHEABLE UNION | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
- SUBQUERY
子查询可以出现在select列表中、where条件中,也可以出现在from列表中。出现在from列表中的子查询为派生表(DERIVED)。如果子查询不依赖主查询中的字段,则称为不相关子查询,select_type为SUBQUERY。SQL执行时,会缓存子查询的查询结果。下面的例子中,子查询中的SQL只需要执行1次,不需要每访问1行数据就重复执行1次子查询。
mysql> explain select a, (select avg(b) from tab ) from tab t1;
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | t1 | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 10010 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 2 | SUBQUERY | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 10010 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
使用EXPLAN ANALYZE命令,可以看到子查询只执行了1次(run only once)。
mysql> explain analyze select a, (select avg(b) from tab ) from tab t1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
EXPLAIN:
-> Covering index scan on t1 using idx_abc (cost=1025 rows=10010) (actual time=0.108..2.54 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Select #2 (subquery in projection; run only once)
-> Aggregate: avg(tab.b) (cost=2026 rows=1) (actual time=3.79..3.79 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Covering index scan on tab using idx_abc (cost=1025 rows=10010) (actual time=0.0235..2.61 rows=10000 loops=1)
- DEPENDENT SUBQUERY
子查询引用了主查询中的字段,则子查询称为相关子查询。MySQL中,相关子查询无法被缓存。对主查询中的每1行数据,都需要执行1次子查询。
mysql> explain select a, (select avg(b) from tab where a=t1.a) from tab t1;
+----+--------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | t1 | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | tab | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | rep.t1.a | 3304 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
使用EXPLAN ANLYZE命令,可以看到子查询执行了10000次(loops=10000)。
mysql> explain analyze select a, (select avg(b) from tab where a=t1.a) from tab t1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
EXPLAIN:
-> Covering index scan on t1 using idx_abc (cost=1025 rows=10010) (actual time=0.0478..3.09 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Select #2 (subquery in projection; dependent)
-> Aggregate: avg(tab.b) (cost=669 rows=1) (actual time=1.39..1.39 rows=1 loops=10000)
-> Covering index lookup on tab using idx_abc (a=t1.a) (cost=336 rows=3337) (actual time=0.023..1.03 rows=3333 loops=10000)
1 row in set, 1 warning (13.94 sec)
MariaDB中,相关子查询也可以cache,对于本例中的SQL,子查询依赖主查询中t1表的字段a,每次t1.a出现新值时,执行1次子查询,并缓存t1.a的值和查询结果。子查询执行的次数取决于关联的外部查询中字段的唯一值数量。
下面这个例子是在MariaDB 10.0的环境中执行得到的。explain extended的warning信息中,<expr_cache> 表示使用了子查询cache。
--这个例子在mariadb 10.0 中执行
mysql> explain extended select a, (select avg(b) from tab where a=t1.a) from tab t1;
+------+--------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+------+--------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | t1 | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9919 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | tab | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | mysql.t1.a | 1668 | 100.00 | Using index |
+------+--------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> show warnings;
+-------+------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+-------+------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Note | 1276 | Field or reference 'mysql.t1.a' of SELECT #2 was resolved in SELECT #1 |
| Note | 1003 | /* select#1 */ select `mysql`.`t1`.`a` AS `a`,<expr_cache><`mysql`.`t1`.`a`>((/* select#2 */ select avg(`mysql`.`tab`.`b`) from `mysql`.`tab` where `mysql`.`tab`.`a` = `mysql`.`t1`.`a`)) AS `(select avg(b) from tab where a=t1.a)` from `mysql`.`tab` `t1` |
+-------+------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- DERIVED
子查询出现在主查询的FROM子句的位置时,select_type为DERIVED。
mysql> explain select t1.*
from tab t1, (select a, avg(b) as avgb from tab group by a) t2
where t1.a = t2.a;
+----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | t1 | ALL | idx_abc | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | ref | <auto_key0> | <auto_key0> | 4 | rep.t1.a | 10 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | DERIVED | tab | index | idx_abc | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
- DEPENDENT DERIVED
如果派生查询引用了主查询中的字段,则select_type为DEPENDENT DERIVED。
mysql> explain select a, (select * from (select avg(b) as avgb from tab where a=t0.a) td) from tab t0;
+----+--------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | t0 | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | <derived3> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 3 | DEPENDENT DERIVED | tab | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | rep.t0.a | 3304 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------------+
- MATERIALIZED
子查询的结果先存储到临时表,查询的其他部分和生成的临时表再关联。
mysql> explain select * from tab where a in( select b from tab);
+----+--------------+-------------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-----------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------+-------------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-----------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ALL | idx_abc | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | <subquery2> | eq_ref | <auto_distinct_key> | <auto_distinct_key> | 4 | rep.tab.a | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | MATERIALIZED | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------+-------------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-----------+------+----------+-------------+
- UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY
如果(不相关)子查询结果无法被缓存,则select_type为UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY。
mysql> explain select * from tab where b > (select avg(b) from tab where b > rand());
+----+----------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+----------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | tab | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index |
+----+----------------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+
导致子查询无法Cache的一些情况:子查询使用了结果不确定的函数(如rand),子查询使用了变量。
- UNCACHEABLE UNION
mysql> explain select distinct a from (select a from tab tb union all select c from tab tc where c > rand() ) tx;
+----+-------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 13346 | 100.00 | Using temporary |
| 2 | DERIVED | tb | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 10010 | 100.00 | Using index |
| 3 | UNCACHEABLE UNION | tc | index | NULL | idx_c | 4 | NULL | 10010 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
TABLE
TABLE这一列说明了一个查询单元的数据是从哪个表获取的。这里分几种情况。
- table是一个真实存在的物理表,这里会显示为表的别名。
<derivedN>,说明是从派生表获取的数据,真实的数据来自ID为N的查询单元<unionM,N>,说明是将ID为M和N的查询单元Union后得到的数据。<subqueryN>,说明是ID为N的子查询物化后得到的数据。
这里的几种情况,在前面的例子中都出现过,你可以回头再看一下。
TYPE
TYPE列显示查询单元的访问路径,你可以根据TYPE列来判断查询单元是否使用了索引。
- system
如果使用了MyISAM存储引擎,并且表中只有1行,则Type为system。
mysql> create table t1_myisam(a int) engine=myisam;
mysql> insert into t1_myisam values(100);
mysql> explain select * from t1_myisam;
+----+-------------+-----------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-----------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1_myisam | system | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-----------+--------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
- const
const表示查询最多返回1行记录。对主键或唯一索引的所有字段都使用常量等值匹配时,type为const。优化器会将type为const的查询单元直接替换为常量表。
mysql> explain select * from tab where id = 10\G
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
- eq_ref
使用主键或唯一索引等值匹配时,type为eq_ref。对于组合主键、组合唯一索引,索引中的每一个字段都需要以等值匹配时,type才为eq_ref。eq_ref访问路径每次最多只返回1行记录。eq_ref和const的区别在于,const使用常量匹配,而eq_ref中,匹配索引字段的值来自驱动表,不是固定的常量。
下面这个例子中,t2表id字段的匹配条件来自驱动表t1的字段a。
mysql> explain select * from tab t1 , tab t2 where t1.a = t2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | ALL | idx_abc | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | rep.t1.a | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------+
- ref
普通索引字段的等值匹配,或主键和唯一索引前缀字段上的等值匹配,类型为ref。对于ref类型的访问路径,执行计划输出中的key列显示了实际使用的索引,key_len显示使用的索引字段的长度,ref字段显示用于匹配的值。
mysql> explain select * from tab where a=1;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | const | 3333 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
mysql> explain select * from tab t1, tab t2 where t1.a = t2.a;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | ALL | idx_abc | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | rep.t1.a | 3304 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+----------+------+----------+-------+
如果索引字段的条件使用了or或in,那么type就不再是ref了。
- ref_or_null
ref_or_null和ref类似,只是额外加了字段为空的条件。对比下下面这两个语句,字段A有not null约束时,type为ref。
mysql> create table tab3 like tab;
mysql> alter table tab3 modify a int;
mysql> insert into tab3 select * from tab;
mysql> explain select * from tab where a is null or a = 1;
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | const | 3333 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
mysql> explain select * from tab3 where a is null or a = 1;
+----+-------------+-------+-------------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab3 | ref_or_null | idx_abc | idx_abc | 5 | const | 3334 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+-------------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
- range
使用索引字段上的范围条件查询数据。范围条件包括 <, <=, >, >=, BETWEEN 等,索引字段使用OR或IN多个值时,类型也为range。对于range访问路径,执行计划中key列显示实际使用的索引名。key_len列显示使用到的索引字段的长度,ken_len取决于使用到的索引字段的数据类型、字段是否可以为空。rows字段显示优化器评估得到的需要在索引中访问的记录数量。
mysql> explain select * from tab force index(idx_abc) where a = 1 or a = 2;
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | range | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | NULL | 6666 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
mysql> explain select * from tab where a = 1 and b between 100 and 200;
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | range | idx_abc | idx_abc | 8 | NULL | 34 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
- index_merge
index_merge会使用多个索引来查询数据,并将通过多个索引获取到的数据取并集或交集,得到最终的结果。执行计划输出中,key字段显示实际参与index_merge的索引。Extra列中的信息显示了实际的索引合并方法,包括sort_union, union和intersect。
如果在执行计划中看到index_merge访问路径,一般要考虑是否可以创建联合索引,将访问路径改成range或ref,或者将SQL改写为union查询。
mysql> explain select *
from t_merge
where (b=1 and d=1) or (c=1 and d between 3 and 5);
+----+-------------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_merge | index_merge | idx_bd,idx_cd | idx_bd,idx_cd | 8,8 | NULL | 210 | 100.00 | Using sort_union(idx_bd,idx_cd); Using where |
+----+-------------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------+
mysql> explain select * from t_merge where a=1 and b=1 and d=1 and c=1;
+----+-------------+---------+-------------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+-------------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t_merge | index_merge | idx_ad,idx_bd,idx_cd | idx_cd,idx_bd,idx_ad | 8,8,8 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using intersect(idx_cd,idx_bd,idx_ad); Using where |
+----+-------------+---------+-------------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------------------+
- index_subquery
index_subquery是执行下面这种类型的子查询的一种方式:
如果子查询中的表tab有合适的索引可以用来检索,则可以使用index_subquery执行路径,对主查询中的每1行记录,执行类似下面的SQL:
mysql> explain select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@qb1) */ * from tab
where a = 1
and b between 100 and 200
and c in (select /*+ QB_NAME(qb1) */ a from tab where b=1 );
+----+--------------------+-------+----------------+---------------+---------+---------+------------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+----------------+---------------+---------+---------+------------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | tab | range | idx_abc | idx_abc | 8 | NULL | 34 | 100.00 | Using index condition; Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | tab | index_subquery | idx_abc | idx_abc | 8 | func,const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+----------------+---------------+---------+---------+------------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */ select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@`qb1`) */
`rep`.`tab`.`id` AS `id`,`rep`.`tab`.`a` AS `a`,`rep`.`tab`.`b` AS `b`,`rep`.`tab`.`c` AS `c`,`rep`.`tab`.`padding` AS `padding`
from `rep`.`tab`
where ((`rep`.`tab`.`a` = 1)
and (`rep`.`tab`.`b` between 100 and 200)
and <in_optimizer>(`rep`.`tab`.`c`,<exists>(<index_lookup>(<cache>(`rep`.`tab`.`c`) in tab on idx_abc))))
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- unique_subquery
unique_subquery和index_subquery类似,区别在于type为unique_subquery时,子查询中的表使用主键或唯一索引来关联查询。
mysql> explain select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@qb1) */ *
from tab
where a=1
and id in (select /*+ QB_NAME(qb1) */ id from tab);
+----+--------------------+-------+-----------------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+-----------------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | tab | ref | idx_abc | idx_abc | 4 | const | 3333 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | tab | unique_subquery | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | func | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+-----------------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
mysql> show warnings\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */ select /*+ NO_SEMIJOIN(@`qb1`) */
`rep`.`tab`.`id` AS `id`,`rep`.`tab`.`a` AS `a`,`rep`.`tab`.`b` AS `b`,`rep`.`tab`.`c` AS `c`,`rep`.`tab`.`padding` AS `padding`
from `rep`.`tab`
where ((`rep`.`tab`.`a` = 1)
and <in_optimizer>(`rep`.`tab`.`id`,<exists>(<primary_index_lookup>(<cache>(`rep`.`tab`.`id`) in tab on PRIMARY))))
上面例子中NO_SEMIJOIN提示是为了阻止优化器使用半连接优化,因为使用半连接优化后,子查询被转换为半连接,就不会出现index_subquery和unique_subquery访问路径了。
- index
index访问路径和ALL类似,主要区别是ALL访问路径需要访问表的每一行数据,而index访问路径是访问索引中的每一行数据。访问路径为index时,key_len字段显示的是所有索引字段的长度总和。一般type为index时,possible_keys总是NULL。
以下2种情况可以使用index访问路径:
情况1:语句使用了覆盖索引,但是又缺少索引字段的查询条件。这种情况下Extra列会显示Using index。
情况2:按索引的顺序读取表的记录,但是无法使用覆盖索引。这种情况下Extra列不显示Using index。
下面的2个例子分别展示了这两种情况。
mysql> explain select a,b,c from tab force index(idx_abc) order by a,b,c;
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
mysql> explain select * from tab force index(idx_abc) order by a,b,c;
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab | index | NULL | idx_abc | 12 | NULL | 9913 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
- ALL
全表扫描,需要访问表中的每一行记录。出现ALL访问路径,可能是因为表上缺少合适的索引,或者是因为SQL语句的写法问题导致无法使用索引,也可能是因为查询中对表缺少合适的过滤条件,或者是索引字段的过滤性不好,需要根据查询语句的情况具体分析。
\因字数限制,学习后面的内容请直接跳转到下一讲
- 笙 鸢 👍(0) 💬(1)
老师,派生表的讲解处,好多DRIVED的写法,是不是写错了??
2024-11-29 - mw 👍(0) 💬(2)
老师好,请教个问题:在选择驱动表的时候 需要过滤where 之后的所有条件之后以数据量小的作为驱动表。 1、那要是where之后的条件没有索引或者无法使用索引的Cardinality进行估算过滤,那选择驱动表的时候就需要扫描全表过滤出符合where条件的数据,然后每个表比较符合的数据量大小,之后选出驱动表吗? 还是说有其他的计算方法。 2、如果where后面同时存在一个表的索引字段条件和非索引字段条件,需要索引字段过滤之后 再过滤非索引字段的条件吗?
2024-10-17